Description
Ipamorelin Peptide
Ipamorelin is a small pentapeptide that binds to the receptor of ghrelin/growth hormone (GH) secretagogue, and research has suggested the peptide to be selective in its mode of action.[1] Ipamorelin, researchers report, does not appear to induce non-specific release of hormones like prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, ACTH, luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, or cortisol. The high specificity of the peptide makes it an ideal model for the study of selectivity in receptor binding. It appears to function through interaction with cognate receptors on the target cell surface and mediates a cellular response. Ipamorelin may induce secretions from the pituitary gland, promoting growth in animal study models.[2] In addition, it may not only trigger the expression of insulin-like growth factor-1(IGF-1) but may also inhibit the secretion of somatostatin.
Specifications
MOLECULAR FORMULA: C38H49N9O5
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 711.85 g/mol
SEQUENCE: Aib-His-D-2Nal-D-Phe-Lys-NH2
Ipamorelin Research
IPAMORELIN AND BONE
Lessened bone density over prolonged periods may lead to fracture. Ipamorelin studies in rats have observed that the peptide may prevent bone loss following prolonged glucocorticoid exposure, and also may induce up to a four-fold increase in bone formation.[3] The researchers also reported that “the decrease in muscle strength and bone formation found in GC-rats was counteracted by simultaneous administration of the growth hormone secretagogue.” The peptide may potentially improve the bone mineral density of both existing and new bones. Additionally, it may possibly mitigate or reverse ancillary impacts such as muscle wasting and fat deposition in visceral organs.
IPAMORELIN AND DIABETES
Studies in murine models of diabetes have suggested an efficacy of Ipamorelin in promoting insulin release from islet cells of the pancreas.[4] Studies suggest that the peptide may mediate the release of insulin through the indirect excitation of calcium channels found on the islet cells. The hypothesized mechanism of Ipamorelin action highlights the limitations of type 2 diabetes and further study may be of interest to researchers.
IPAMORELIN AND CORTICOSTEROIDS
Glucocorticoids are the kind of corticosteroids that are commonly considered to exert an anti-inflammatory response in diverse conditions ranging from cancer to autoimmune disease. Ancillary action has also been reported. Over long durations, a higher concentrations of hormones may be required to overcome physiological ancillary impacts. Researchers studying the action of Ipamorelin have suggested the peptide’s potential to decrease certain unintended impacts associated with glucocorticoid exposure.
IPAMORELIN AND MUSCLE CELLS
Growth hormone (GH) and GH secretagogues such as Ipamorelin may decrease any catabolic action of glucocorticoids on muscle cells. Studies on Ipamorelin posit that it may help to reestablish the nitrogen balance and reduce nitrogen wasting in the liver of rats that were exposed to glucocorticoids. The molecule exhibited the potential to overcome muscle wasting and loss of bone density in research models exposed glucocorticoids.
IPAMORELIN AS GHRELIN RECEPTOR PROBE
The peptide appears to bind strongly to the ghrelin receptor and may act as a selective agonist. Interestingly, the ghrelin receptor has been observed to increase cardiac failure and certain types of cancer, including carcinomas. Researchers have proposed studying Ipamorelin as a probe in positron emission tomography (PET) scans to help diagnose research models. [5] Further research is ongoing.
IPAMORELIN AND POST-OPERATIVE ILEUS
Post-operative Ileus (POI) is a condition characterized by an inability of the subject to accept oral nutrition as the GI system stops functioning. Ipamorelin has been studied in multiple proof-of-concept studies to determine its potential to reduce POI. It was found to shorten the time of uptake of the first meal by about 12 hours in POI models.[6] The researchers concluded that “ipamorelin accelerates gastric emptying in a rodent model of postoperative ileus through the stimulation of gastric contractility by activating a ghrelin receptor-mediated mechanism involving cholinergic excitatory neurons.” Some of the research observations in this and other studies suggest that residual radiolabeled food remaining in the stomach of rats with POI was less after the influence of Ipamorelin, even when compared to rats without POI.
Additionally researchers noted that when exposed to Ipamorelin, the geometric location of the food was observed to be similar for both rats without POI and those with POI. Furthermore, the radiolabeled food was located more distally in the GI tract and is similar to rats without POI, after Ipamorelin was given to rat models of POI.
Disclaimer: The products mentioned are not intended for human or animal consumption. Research chemicals are intended solely for laboratory experimentation and/or in-vitro testing. Bodily introduction of any sort is strictly prohibited by law. All purchases are limited to licensed researchers and/or qualified professionals. All information shared in this article is for educational purposes only.
References
- Raun K, Hansen BS, Johansen NL, Thøgersen H, Madsen K, Ankersen M, Andersen PH. Ipamorelin, the first selective growth hormone secretagogue. Eur J Endocrinol. 1998 Nov;139(5):552-61. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1390552. PMID: 9849822.
- Johansen PB, Nowak J, Skjaerbaek C, Flyvbjerg A, Andreassen TT, Wilken M, Orskov H. Ipamorelin, a new growth-hormone-releasing peptide, induces longitudinal bone growth in rats. Growth Horm IGF Res. 1999 Apr;9(2):106-13. doi: 10.1054/ghir.1999.9998. PMID: 10373343.
- Andersen NB, Malmlöf K, Johansen PB, Andreassen TT, Ørtoft G, Oxlund H. The growth hormone secretagogue ipamorelin counteracts glucocorticoid-induced decrease in bone formation of adult rats. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2001 Oct;11(5):266-72. doi: 10.1054/ghir.2001.0239. PMID: 11735244.
- Adeghate E, Ponery AS. Mechanism of ipamorelin-evoked insulin release from the pancreas of normal and diabetic rats. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2004 Dec;25(6):403-6. PMID: 15665799.
- Childs MD, Luyt LG. A Decade’s Progress in the Development of Molecular Imaging Agents Targeting the Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor. Mol Imaging. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1536012120952623. doi: 10.1177/1536012120952623. PMID: 33104445; PMCID: PMC8865914.
- Greenwood-Van Meerveld B, Tyler K, Mohammadi E, Pietra C. Efficacy of ipamorelin, a ghrelin mimetic, on gastric dysmotility in a rodent model of postoperative ileus. J Exp Pharmacol. 2012 Oct 19;4:149-55. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S35396. PMID: 27186127; PMCID: PMC4863553.
- Sigalos JT, Pastuszak AW. The Safety and Efficacy of Growth Hormone Secretagogues. Sex Med Rev. 2018 Jan;6(1):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Apr 8. PMID: 28400207; PMCID: PMC5632578.

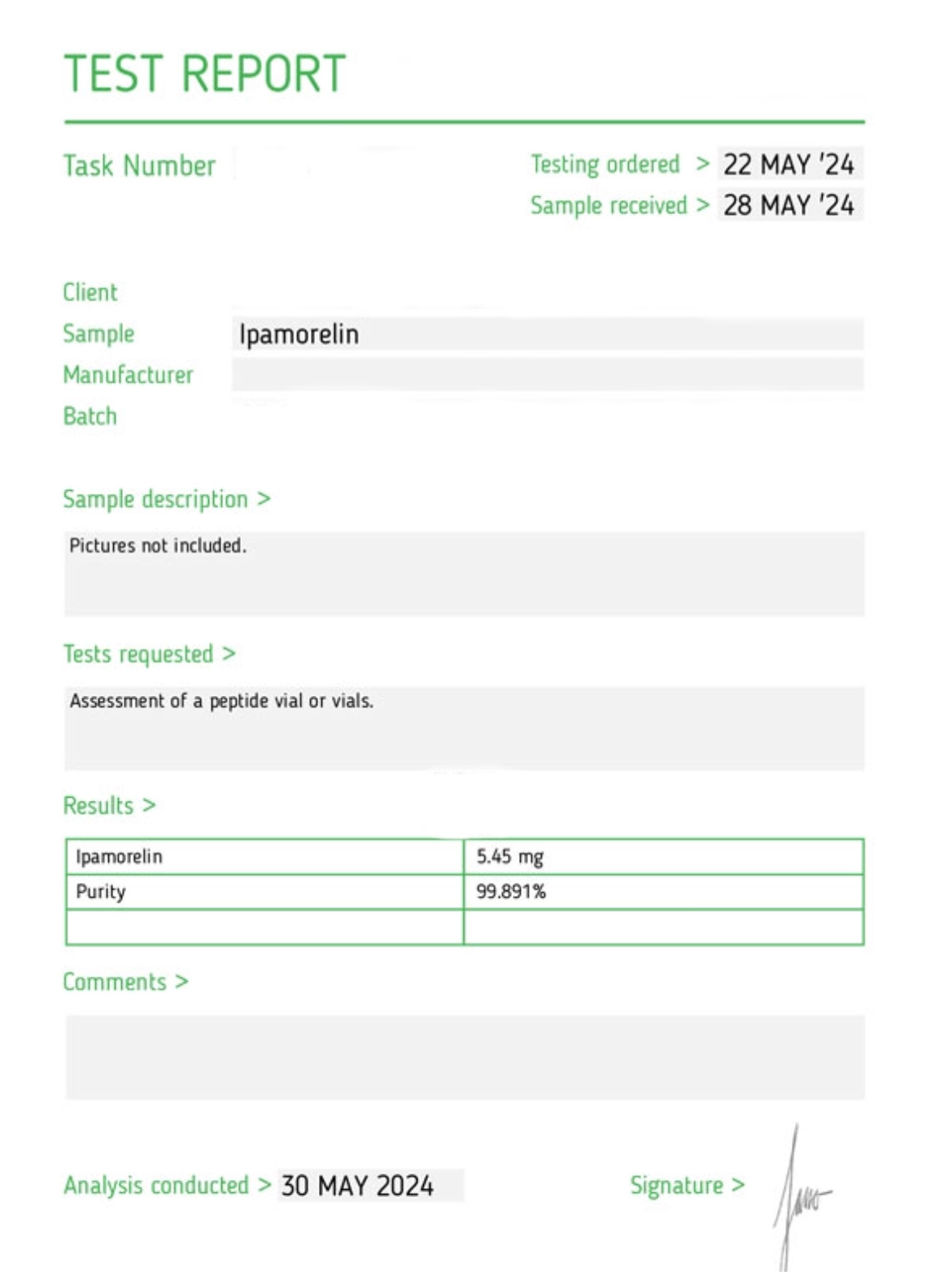
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.